Article
Scrum and advantages of a physical scrum board
What is scrum?
Scrum has been steadily gaining popularity since the early nineties, especially among software developers and more recently within other profession groups. These include hardware developers, logistics, education, marketing teams and other teams that need flexibility in their planning.
Although being developed for quickly changing environments of software development at first, it has proved to assist other groups when tackling projects that require flexibility and quick adaptation to ever changing requirements. This is also known as being agile. Quite in contrast to the traditional way of sequential developing, which doesn’t allow many changes in the planning along the way. Especially when this includes integrating new technologies.
With scrum, project teams are able to respond to ongoing technological advances by re-evaluating the progress and requirements before each sprint. Rather than hindering the process with the integration of new techniques, each product increment is a set of consolidated team efforts and techniques achieved in a sprint. With the ultimate goal of gaining more understanding of needs as the projects goes along, delivering the best possible potentially shippable product and match wishes of the stakeholders.
What is a sprint?
A sprint in scrum is a timebox of a month or less with a clear focus on a particular task that must be tackled by the scrum team.The main goal is to deliver a potentially shippable product by the end of each sprint. Which means that each product increment must be well tested and function by all means. After each sprint the scrum project management team and stakeholders gather for a sprint review. They evaluate the work that was completed, the work that was not completed and to present the completed work. During the sprint review work for the next sprint is defined and prioritized.
Scrum master
The scrum master facilitates meetings and takes care of the team staying on task by warding them off the stakeholders. Which could potentially distract the team with irrelevant request.
Scrum teams
Scrum teams work best with 3 to 9 team members and consist of experts – each in their own field to form a cross-functional team.
Daily meetings
During the daily standup meeting of 15 minutes each team member shares with the team:
- what he/she has been busy with since the last daily meeting;
- what is he/she going to work on until the next daily standup;
- and discuss any impediments that are preventing him/her from accomplishing his/her tasks.
Above all daily scrum meetings are needed to give the team members a platform to voice their opinions, steer team efforts and increase productivity.
Advantages of a physical scrum board
While the tendency to manage scrum online perpetuates, it may create more distance between the team members than you may wish for. Opposed to bringing them together to form a team in which they feel free to voice their opinions, an online platform may generate more individual work islands than efficient work teams.
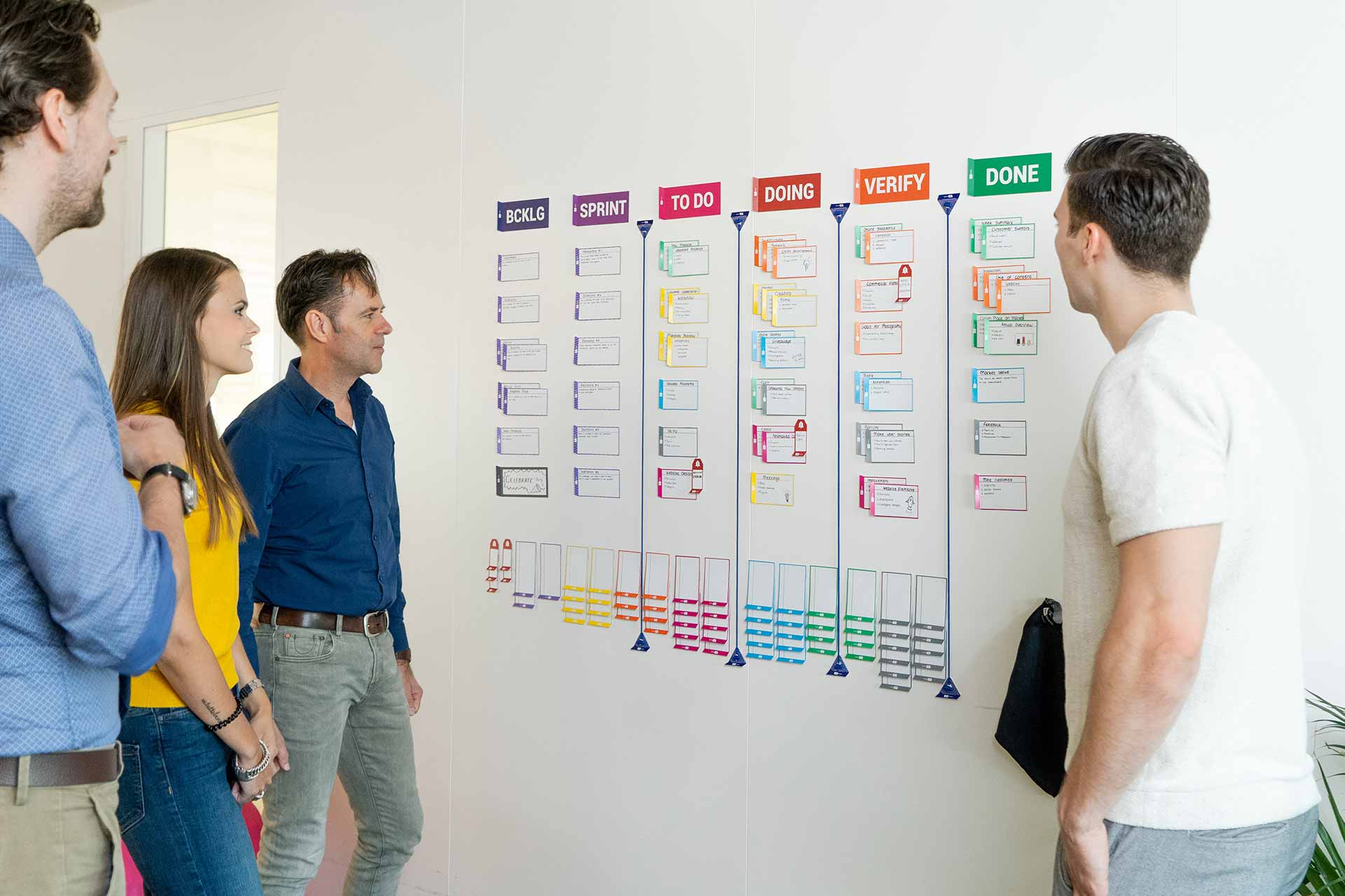
At PATboard we believe in a close team collaboration which includes a physical scrum board. A physical board motivates the team to gather, discuss and collaborate. By motivating them to exchange expert views this leads to better communication, more ownership, better products and less unwanted delays. A physical scrum board ultimately facilitates cross pollination of knowledge within the team and agile development of the best version of shippable product.
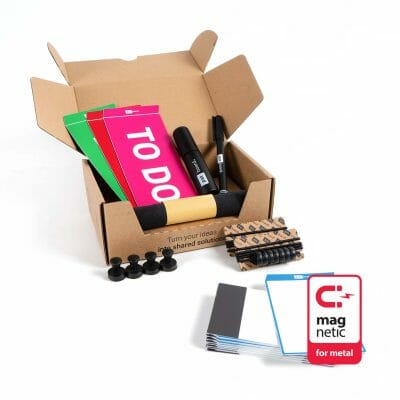
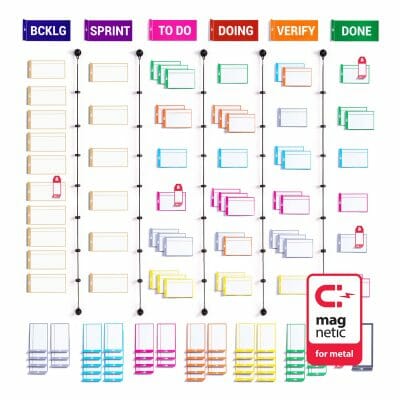
To facilitate the need for a physical scrum board and bring more fun to workplaces, the PATboard team (full of agile enthusiasts) has designed a range of colorful and durable tools that support the idea. Among our products you will find magnetic sticky notes – Task Cards, Story Cards, Impediment Cards, Column Cards and column dividers PATlanes. And to make work even more fun, you can use the sticky team icons to assign each member a task. Our products are reusable, stackable and above all a real Dutch design.

What do I need to set up a physical scrum board?
up to 8 team members
– Magnetic board
– PATboard scrum board full tool set or equivalent
Which scrum board tool set should I choose?
– Full tool set (up to 8 team members)
– Basic tool set (up to 4 team members)
– Home tool set (domestic use)
How big should my scrum board be?
How big your scrum board should be depends on how many columns you want to use, how big your team is and how many tasks you have during one sprint. Although it might sound complicated, it’s not. The main thing you should take into consideration is the width of your board.
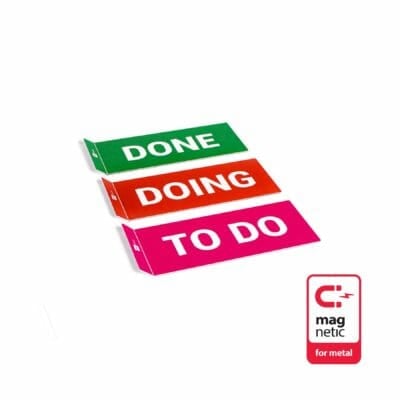
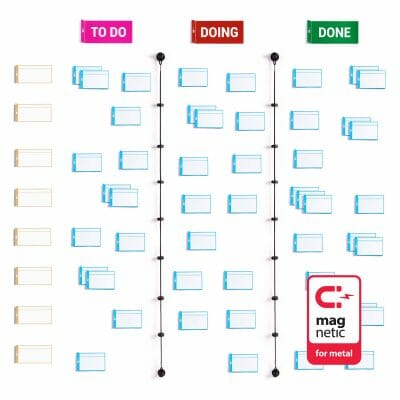
We advise to assign 30-40 cm to each column in order to have enough space below for placing and stacking TASKcards. This adds to 90-120 cm width when using 3 column cards (TO-DO, DOING, DONE) or 210-280 cm width when using 7 column cards (BACKLOG, SPRINT, TO-DO, DOING, VERIFY, DONE, Blank). If your whiteboard is wide enough it usually also is high enough.
Shop whiteboards for agile scrum and kanban in our web store >
Custom work
In case you don’t find the right tools for your physical board, do let us know. We will be happy to help you with our customized solutions.
PATboard – your one-stop shop for physical agile, kanban and scrum office supplies!